Hello and welcome to another lesson of the Basic SEO course! Today, we’re going to explore how search engines display results and dive into the world of SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages). We’ll break down what a SERP is and how organic search results are shown by search engines like Google. It’s going to be fascinating, so let’s get started!
What Happens When You Search on Google?
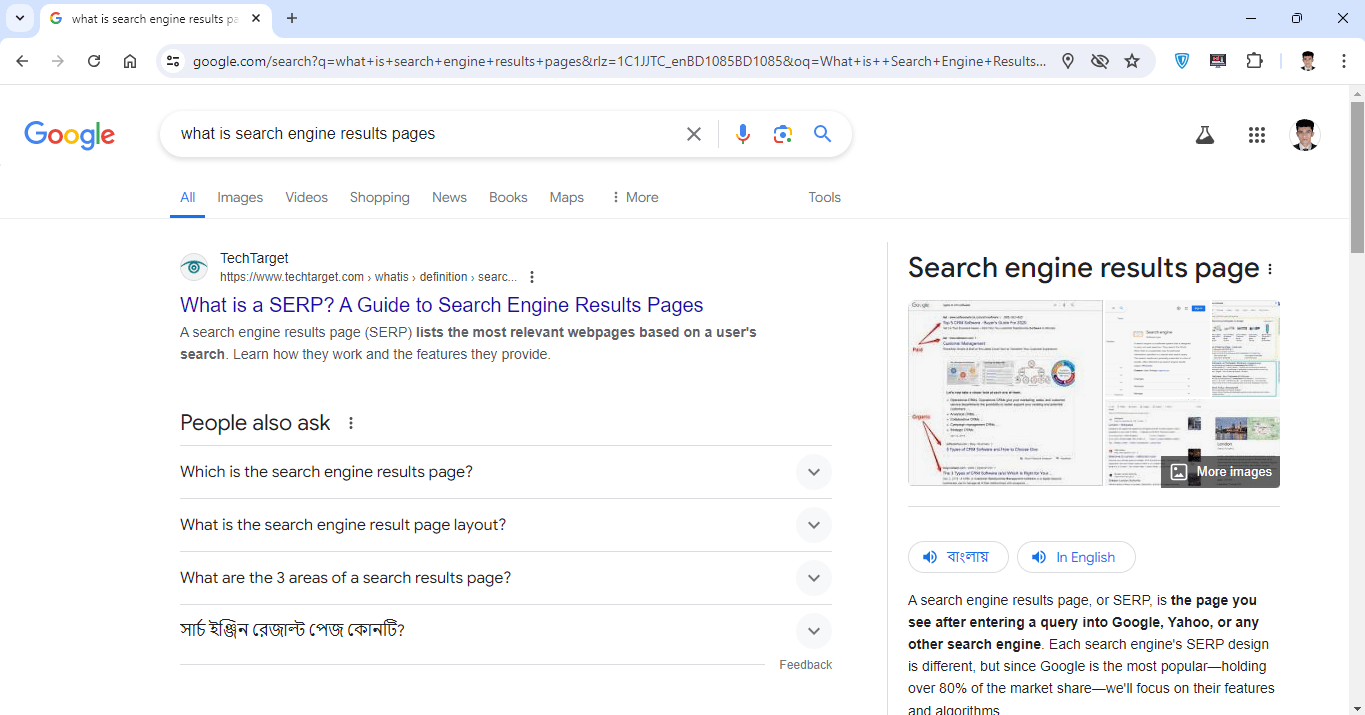
When you type a query into Google, the search engine analyzes it to figure out what you’re looking for. It then finds the best results, ranks them, and presents them to you. The page you see after this process is the search engine results page—also known as the SERP.
A SERP is essentially a page of recommended content generated by a search engine based on a user’s query. You’ll notice that the SERP is a list of blue links to pages that match the subject of your query. However, there may also be additional elements on the page such as images, videos, maps, advertisements, featured snippets, a knowledge graph, and more.
Understanding the SERP Structure
We’ll be discussing all these elements in detail today and in the next lesson. Now that we’ve covered the structure and concept of the SERP, let’s dive into organic results and their features. Remember, free organic search results have nothing to do with advertising. It’s the search engine that selects web pages and determines their position in the list.
Google considers page relevance (how well the content matches the search query) and its own evaluation of quality to decide the order of the pages in the SERP. Most of the results on a search engine results page are organic and not ads—Google is recommending sites to users with no commercial gain, often in the form of blue links, typically ranging from 5 to 10 per page.
Organic Results and Snippets
Each page in the organic results is represented by a small block (snippet) consisting of a blue link to the page, a header, and a short description. Sometimes, you might see rich snippets, which display additional information besides the brief summary. For instance, a snippet might include sitelinks that help users quickly navigate to important sections of a website. You may also see company ratings according to user reviews or a snippet with a series of related questions. You’ll encounter many of these rich snippets when searching for things like products, recipes, books, films, learning courses, and job openings.
Pay-Per-Click and Google Ads
Now, let’s look at pay-per-click (PPC) and Google Ads. These ads (contextual ads) appear in the SERP, usually for commercial search queries related to a product or service. They look similar to the blue links in organic results but can be distinguished by the “Ad” mark. Contextual ads appear above and below the list of organic search results.
Google has a service called Google Ads for setting up ad campaigns. For a contextual ad to appear in the SERP, advertisers must specify appropriate keywords in their settings. Contextual advertising operates on a PPC principle, meaning the advertiser pays for each user who clicks through to their site.
Contextual Ads and Shopping Ads
In addition to text ads, you may also see contextual shopping ads in the search results. These appear as picture blocks below the query bar or to the right of the search results. The SERP itself includes different search categories, or verticals, which you can see at the very top, right below the search bar. The first and main section is “All,” where you see a list of 8 or 9 pages presented as blue links, often alongside results from other search categories on the SERP.
Exploring Different Google Search Categories
The other tabs might change their position in the navigation menu or hide behind the More button, depending on the request. Google supports searching by Images, Videos, News, Maps, Flights, Finance, Books, and Shopping. Let’s take a closer look at each:
- Images: Click on this tab to see only images.
- Videos: This tab shows only videos.
- News: Here, you’ll find relevant, mostly recent articles on the subject.
- Maps: Clicking on Maps takes you straight to Google Maps, where you can find routes, save locations, and zoom in on maps. You can view shops, establishments, hospitals, and other locations in your area or any other area.
- Shopping: This section displays products with prices, ratings, and other characteristics. Filters on the left help you sort the results, such as setting price ranges or selecting screen resolutions, depending on the product. Clicking on a product takes you to the retailer’s site for more details and the option to purchase.
- Finance: This section provides information on stocks, exchange-traded funds, and other assets, including news, statistics, and market trends.
- Books: In the Books tab, you’ll see Google Books, which is Google’s database for books and authors. Clicking on a book directs you to a dedicated Google site where you can see details about the book and often have the option to buy its electronic version.
- Flights: The Flights tab takes you to a special Google service for viewing flights, selecting dates and destinations, and booking directly with airlines.
Related Queries and Navigation
At the bottom of the search results, you’ll often find a Related Queries box with query variations related to the user’s initial search. This provides a list of suggestions to continue your search without typing another query, simply by clicking on an option. Almost at the bottom of the SERP, there’s an option to go beyond the first page to other result pages. Finally, at the very bottom, you’ll find the footer block, which shows your location. This might seem unimportant, but it affects the relevance of the results Google shows you, which is crucial for your SEO strategy.
Understanding Google Help and Policies
Clicking on the Help tab will take you to the Google Search help center, where you can find answers to questions about using Google Search. The Privacy and Terms of Use sections explain what data Google collects and why. Reading these sections with a marketer’s perspective can provide insights into Google’s ranking approach.
Mobile Search Results
We can’t overlook mobile search results. We use phones a lot—more than desktop computers, especially outside of work. As of 2021, Google prioritizes mobile queries, and search results are increasingly tailored to mobile-first. Mobile search results have unique characteristics. The mobile SERP differs in website rankings, and searching the same query on a phone versus a computer yields different results. Unlike the desktop version, the mobile SERP has no pagination, just a “More results” button to load additional results.
Favicons are displayed at the top of the snippet on mobile, along with the resource name and link. The snippet itself often includes the main picture of the page or a video. For app-relevant searches, you’ll see an installation box for the app. The mobile version is also easy to use with voice activation—simply press the microphone and speak your query.
Discover, Snapshot, and Collections
In addition to the standard search, the mobile version includes tabs such as Discover, which shows weather forecasts and breaking news; Snapshot, which lists things to do like flight reminders; and Collections, which shows saved items like pages, locations on maps, images, and more. These features provide a clear direction for where Google is heading with search and how SEO needs to adapt in the future.
Wrapping Up
That wraps up today’s lesson. I hope you’ve gained a lot of valuable information. In the next lesson, we’ll continue discussing search engine results and explore rich elements in Google’s SERP—the so-called “SERP features.” Thanks for reading, and I’ll see you in the next lesson!