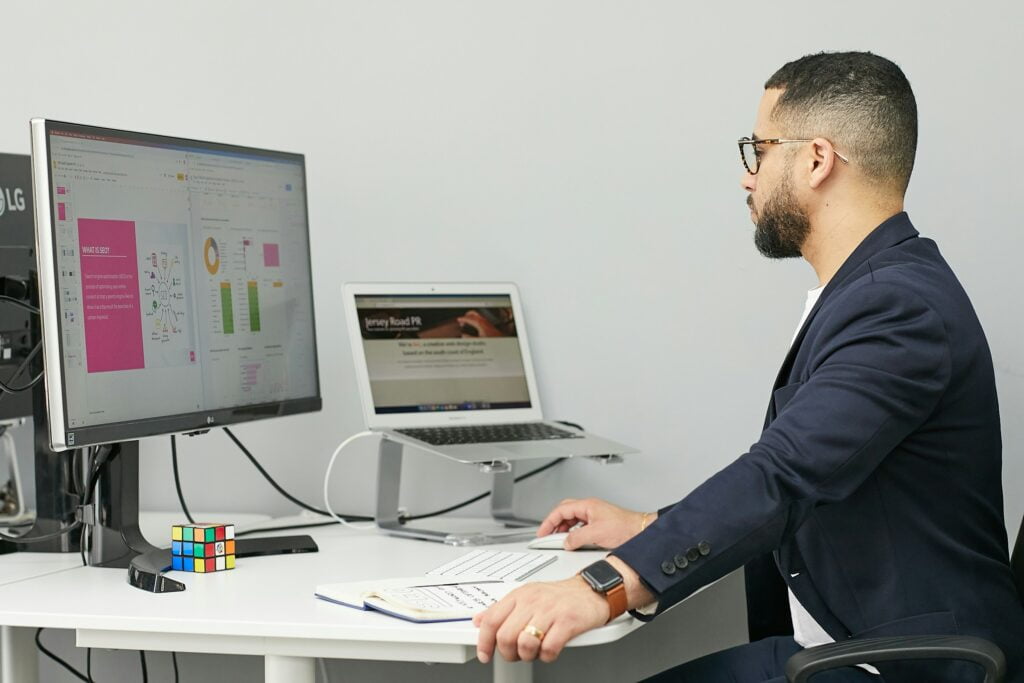
Link building is arguably the most challenging part of SEO. It requires technical prowess, a creative approach, and just straight-up grit and grind. If you’re a beginner to link building or you’ve tried building links without much success, this tutorial will help you get backlinks efficiently so you can rank your pages higher on Google.
The Two Dominant Views on Link Building:
Link building has built all sorts of reputations. There are generally two dominant views. One party of SEOs lives and dies by it. The opposition considers it to be a spammy tactic. To come to a conclusion, we need to define what link building is.
What is Link Building?
By definition, link building is the process of getting other websites to link to a page on your website. These hyperlinks are called backlinks. While the end result might make sense conceptually and seem simple, the part that people don’t understand and can’t seem to get right is the process. This ultimately boils down to execution.
The reason why execution is tough is because people focus on the end result: getting backlinks to their pages. But the process is actually very relational, and relationships are built by humans, not “borrowed” templates from videos and blog posts.
So, let’s redefine link building and set the tone for the rest of this tutorial.
Link building is the process of building relationships with other relevant site owners who want and will link to your content because it enhances theirs. This definition includes relationships, relevance, and a value exchange.
Why Link Building is Worth the Effort?
Since effective link building is tough, you need to understand why it’s worth the effort. In short, backlinks are used by search engines like Google to help rank web pages. It’s been this way since 1998 when Google created PageRank. PageRank is a mathematical formula that judges the “value of a page” by looking at the quantity and quality of other pages that link to it.
Google confirms the importance of backlinks on their “How search works” page. Under their “Ranking useful pages” heading, they state: “If other prominent websites on the subject link to the page, that’s a good sign that the information is of high quality.” We also found a clear correlation between organic traffic and backlinks from unique websites in our study of over one billion web pages.
So while getting backlinks may be harder than, let’s say, creating a blog post, they’re absolutely critical if you want to rank for competitive phrases. You might think, “Well, so and so said not to focus on link building because high-quality content always attracts links.” Well, how do you get that content in front of people in the first place? Unfortunately, the concept of “if you build it and they will come” is just pure fantasy.
Or you might have heard other people say, “I get tons of traffic without building backlinks, so no need to go through the struggle.” Yes, it’s possible to rank pages without backlinks, but let me say this one more time: backlinks are absolutely critical if you want to rank for competitive phrases. And competitive phrases are usually the ones that’ll drive the most traffic and revenue for your business.
For example, queries related to SEO are extremely competitive, but they’re also very lucrative. If you take a look at our blog’s backlink growth in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer, you’ll see that the growth curve almost mirrors that of our organic traffic. They’re rising together.
How to Get Backlinks?
There are three ways to get backlinks. You can create them, buy them, or earn them. Let’s go through each method.
- Creating Backlinks: Creating backlinks means manually adding links to your site. This can be done by adding your website to directories, leaving comments on blogs, or adding a website to your social media profile. Anyone can do this with minimal effort, so they’re not that effective from an SEO and ranking perspective.
- Buying Backlinks: Buying backlinks is exactly as it sounds. You pay webmasters or authors a fee and in return, they’ll link back to a page on your site. This is against Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and can potentially result in a penalty. That could be anything from losing ranking positions or, even worse, getting your pages removed from Google’s search index. Also, buying links isn’t exactly cheap. We contacted 250 websites to ask if they sell links, and we found that the average cost of buying one was nearly $353. And no, we didn’t buy any.
- Earning Backlinks: The final way to get backlinks is to earn them. This is usually done by emailing other website owners and editors and asking them to link to you. This is the hardest method of the three, but generally speaking, the harder it is to obtain a link, the more valuable it’ll be. For that reason, we’ll focus on earning backlinks through email outreach.
What Makes a Good Link?
Not all links are created equal. Some will help propel your pages to the top of Google, while others can actually hurt your site. So, what makes a link actually good? There are two main categories you should look at: relevance and authoritativeness.
Relevance:
Ideally, you want to get backlinks from relevant websites and pages. For example, if you have a page on the best USB microphones, getting a link from a page on the topic of video conferencing would be much more relevant than a link on a page about gardening tips. This also plays out at the website level. Getting a link from a tech site like Cnet would likely carry more weight than one from a recipe site like All Recipes.
Authoritativeness:
Authority represents the “link power” a web page has, relating to how PageRank works. Both the quantity and quality of links matter. So, the more quality links a page gets, the more PageRank it earns. PageRank doesn’t appear out of thin air; it comes from other pages. Pages with authority can pass it to other pages through hyperlinks. The more PageRank a linking page has, the more it can pass to those outbound links.
For example, let’s say page C has two links: one from page A and one from page B. Page A is stronger than page B and also has fewer outgoing links. Feed this information into the PageRank algorithm, and you get the PageRank of page C.
Google doesn’t provide PageRank or website authority scores, but Ahrefs has two metrics that try to quantify it. Domain Rating represents the overall strength of a website’s backlink profile, and URL Rating represents the overall strength of a page’s backlink profile. We have a full video on assessing high-quality backlinks, so I’ll link that up for you in the description.
The Anatomy of a Hyperlink:
There are three basic parts to a link that matter in SEO: the destination URL, anchor text, and the “rel” attribute or lack of one.
Destination URL:
The destination URL is simply the URL the person will visit when the link is clicked.
Anchor Text:
The anchor text is the clickable word, phrase, or image attached to the link. Google uses anchor texts to better understand what a page is about and what terms it should rank for. Building lots of links with keyword-rich anchors is classified as a link scheme and may result in a Google penalty as it looks unnatural.
For example, if you had a post on the best wireless headphones and had a hundred links pointing to it where the anchor texts were all “best wireless headphones,” then it would look quite unnatural. People often use anchors such as the company’s brand name, the title of the page, the URL, or phrases like “click here.”
Here’s some proof. If we look at the anchors of backlinks pointing to our data study on featured snippets, you’ll see varying anchor texts like “old studies,” “ahrefs,” “research,” and even specific stats like “99.58%,” “8.6% of all clicks,” and so on. In fact, there are only 14 websites that have linked to us using the anchor text “featured snippet.” With most earned links, you have very little or no control over the anchor text, so over-optimization isn’t something you really need to worry about.
Rel Attribute:
Some links contain a “rel” attribute, which is intended to tell crawlers the relationship between the linking page and the linked page. The three “rel” values you should know about when it comes to link building are “nofollow,” “UGC,” and “sponsored.” Historically, nofollow links told Google that the linking page would rather not associate themselves with the linked page. For that reason, Google didn’t transfer “authority” through those links.
Google added a couple of other “rel” values: “UGC” (user-generated content) and “sponsored” (signifies a paid link). They also announced that going forward, they would look at these link attributes as “hints,” meaning they may pass value through them at their discretion.
If a link doesn’t have any of these “rel” values, then it would be called a “followed” link, meaning the link can pass PageRank and help boost your rankings. Seeing as this is still relatively new, I’d recommend focusing on building “followed” links, although that’s only partially within your control.
Link Placement:
Prominent links are more likely to be clicked, and it’s believed that Google takes this into account when determining how much authority a link transfers. For instance, an editorial link is more likely to be clicked than a link in the footer. All else being equal, the former would be better than the latter.
The Creative Part of Link Building:
Link building is both an art and a science. There’s a creative part required, including content creation and getting creative with your email pitch. With enough willpower and determination, it’s possible to build links to any kind of page, but life is a lot easier when you have something that people actually want to link to.
Linkable Content:
There are a couple of key attributes that make something more link-worthy than others. Non-commercial content that’s highly useful is usually more deserving of a link. Helpful blog posts are always good. For example, Healthline gets tons of links to their concise, vetted blog posts. Other types of content that do well include calculators and tools. We have a free backlink checker that’s earned tens of thousands of links, Nerdwallet’s retirement calculator has earned thousands of links, and Bank Rate’s mortgage calculator has around 4,000 backlinks. Data studies are also very linkable.
For example, our blogger survey has earned links from 730 referring domains, and our study on featured snippets has links from over 2,000 referring domains. Case studies also work well. Our Zero Search Volume case study has links from over 430 referring domains.
The Pitch:
Now, for the second part, which is your pitch. If you created a fantastic piece of content but no one knows it exists, then it won’t attract any backlinks. Instead, you need to reach out to authors and editors and let them know you exist. This part of the process can also be quite creative, as there are always multiple ways to find link prospects and good reasons to contact them.
There are generally three things you can do to improve your link conversion rates.
- Personalization: Using someone’s name in a mass email template isn’t enough. Show them that you actually know who they are, what they do, and what their website is about. For example, mentioning a recent post they wrote can help break the ice.
- A clear reason for the email: For example, if you’re doing email outreach for link building, a clear reason would be something like a broken link on their site, a piece of content that doesn’t back up a point well, or simply reaching out to tell them about your resource because it would enhance their content. The best reasons for emailing are those that will benefit the prospect and not just yourself.
- A value exchange: People are busy, and adding a link to their page means they’ll have to make an edit. If you can’t give a clear reason for emailing them, then think of a way you can add value to their site. For example, you might offer to write a guest post, send them some free content, or offer to share their content on social media.
Link Building Strategies:
Are you planning to start a link building campaign? If so, you’ll want to check out these top link building strategies to build some serious high-quality backlinks. Hi there, I’m Eduard Dziak from B2BDM, and today I’m excited to share with you 13 link building strategies. Some are creative, some are advanced, and some are classic techniques that still work like a charm if done right.
So, without further ado, let’s dive in!
1: Guest Posting:
The first link building strategy on our list, and definitely one of the most well-known and still very effective, is guest posting. This method has been around for ages and is widely used by link building experts and marketing agencies to acquire high-quality backlinks.
For example, Leo Widrich, the founder of Buffer App, used guest posting to acquire 100,000 customers in the first 9 months. Similarly, Brian Dean has written over 200 guest posts and now ranks for some of the most competitive keywords in the SEO niche. However, Google is not a fan of guest posting for links. According to John Mueller, guest posting for links results in unnatural links, and Google has started devaluing them. This doesn’t mean guest blogging is dead; it just requires a smarter approach.
2: Resource Link Building:
The second effective strategy is resource link building. This approach helps you acquire many high-quality backlinks by targeting resource pages that recommend useful external resources.
Reason 1: It’s one of the easiest link building strategies if you invest time in content marketing and blogging. Resource pages list valuable resources on a specific topic. For instance, Naven’s page on “Best SEO Blogs to Read” curates top SEO blogs, showcasing why resource link building can be so effective if you’re dedicated to content marketing.
Reason 2: The outreach process is simpler, as many resource pages include contact information. For example, Naven’s page has his email listed for outreach, making it easier than finding a contact for guest posting.
Reason 3: Pitching for resource page links is generally easier because these pages are designed to feature great resources. By providing valuable content, you can more easily convince page owners to include your site.
Remember to highlight how your resources can help keep their page updated, as regular updates are valued by Google.
3: HARO Link Building:
The third strategy on our list is HARO (Help A Reporter Out) link building. HARO allows you to earn high-quality backlinks with minimal effort by responding to journalist queries. Register at HARO to receive journalist queries three times a day, Monday to Friday. By selecting queries relevant to your industry, you can provide expert insights and earn backlinks.
4: Purchasing Expired Domains:
Another effective strategy is purchasing expired domains with high authority. This approach is more advanced and can be risky if not done correctly.
Technique 1: Start a website with an expired domain instead of a new one. This gives you an SEO advantage by leveraging existing backlinks.
Technique 2: Broken Link Building. Find expired domains, recreate their content, and reach out to those linking to the old site to update their links to your new content.
5: Skyscraper Technique:
The Skyscraper Technique, created by Brian Dean, involves creating superior content compared to your competitors. Analyze SERPs for your target keyword, identify what topics your competitors cover, and create better, more comprehensive content. Afterward, reach out to bloggers who link to your competitors, mention those featured in your content, and contact those who target similar keywords.
6: Podcast Interview Link Building
Podcast interviews are a fantastic strategy for acquiring high-quality backlinks. Find relevant podcasts, offer to be a guest, and share your expertise. To discover podcasts, use Google searches or keyword research tools like SE Ranking.
7: Social Proof Link Building:
Social proof link building involves exchanging a backlink for a review or testimonial. While this strategy can be effective, it borders on grey-hat SEO and may not be compliant with Google’s guidelines. Focus on providing genuine reviews for products or services you use to increase your chances of getting a backlink.
8: Links Exchange:
Exchanging links can be risky as it often goes against Google’s guidelines. You can engage in reciprocal or non-reciprocal link exchanges, but be cautious and ensure it doesn’t look excessive or manipulative.
9: Unlinked Mentions:
Claiming unlinked mentions of your brand involves finding instances where your brand is mentioned but not linked. Use Google searches or tools like BrandMentions to find and request backlinks from these mentions.
10: Competitor Backlink Analysis:
Analyze your competitors’ backlinks to understand their strategies and identify opportunities. This technique helps you gauge what’s required to compete effectively in your niche.
11: Social Fortress Link Building:
Build a social fortress by registering on various social media platforms to obtain backlinks. While these are often nofollow links, they signal to Google that your business is legitimate and can aid in building trust.
12: Link Roundups:
Link roundups involve getting featured in curated lists of content. Search for roundup posts in your niche using Google Search Operators or analyze where your competitors have been featured.
13: Industry Study and Research:
Creating industry studies and research can generate significant backlinks. These studies are often cited and shared widely, leading to numerous backlinks. While they can be expensive and time-consuming, the rewards can be substantial.
These tactics, along with others, can help you build links effectively. If you enjoyed this article, subscribe for more actionable SEO and marketing tutorials. See you in the next article!